Table of Contents
Several months ago, Microsoft released the ninth version for Windows 10, better known as Windows 10 2004. This version is also known as 20H1 or as the “May 2020 Update”. Normally the spring editions are 1803, 1903 and so on. What is the reason this Windows 10 spring edition has been named 2004?
Microsoft: The month indicator for this release is 04 instead of 03 to avoid confusion with Windows release in the year 2003
This release is a Semi-Annual Channel (SAC) version, which means this version receives feature updates twice a year. Important to know is that all spring editions will receive servicing for 18 months. Fall editions (Enterprise and Education only) will receive 30 months of servicing. In this research the performance impact of Windows 10 2004 will be validated.
What’s new in Windows 10 2004?
Let’s have a look at some of the new features that have been added to Windows 10 2004, before dealing with the results.
Notepad, Paint and Wordpad are optional
These built-in applications always have been installed. Now they are optional.
Virtual Desktop Renaming
Normally it would be called “Desktop 1” “Desktop 2”. Now there is a possibility to give your Virtual Desktop a name.
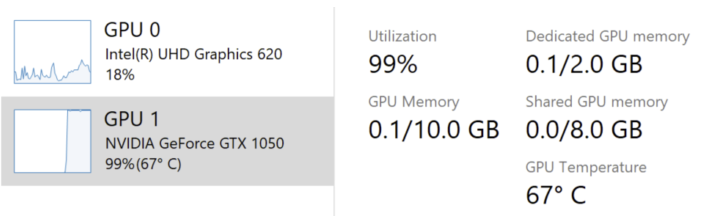
Task manager shows the GPU temperature
The Windows Task manager has the capabilities to display the GPU temperature, as shown in the image below.
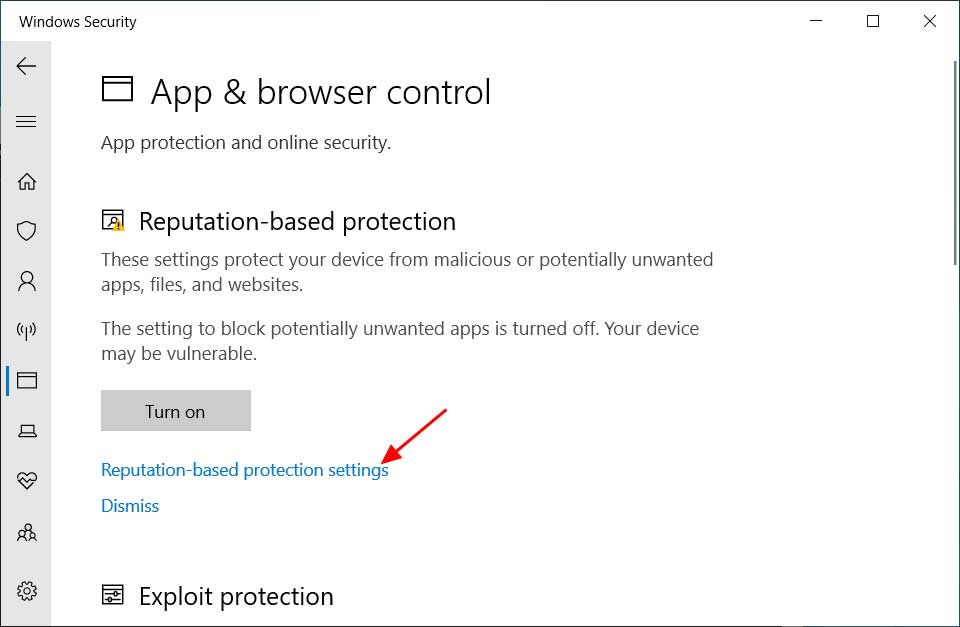
Reputation-based protection settings
Previously this feature was “hidden” and available via Windows Powershell with Set-MpPreference. Since the release of Windows 10 2004 it is possible using the Windows Security app.
Other improvements
More improvements and additions come with Windows 10 2004 update and are listed below:
- Wi-Fi 6 and WPA3 support;
- Cortana will have a new chat-based experience where you can type in your question and interact with the digital assistant;
- Reset this PC from the cloud allows users to reset their PC using Windows files downloaded from Microsoft’s servers;
- Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL2). With this release, Windows 10 uses WSL2 as its default version.
For more information please visit the following blog. For an overview of the features and functionalities that have been removed, please visit the Windows documentation.
Infrastructure and configuration
This research has taken place on the GO-EUC infrastructure which is described here. The parent Windows 10 deployments are build with MDT using an identical task sequences. The only difference between the task sequences is the Windows 10 build. The machines are provided with Citrix Virtual Apps & Desktops version 1912 for both infrastructure and the VDA. The test machines are deployed using Citrix MCS with a default configuration of 2 vCPU’s and 4GB of memory.
Please note: there are some known issues with Citrix CVAD 1912 in combination with Windows 10 2004, which are described here.
The Windows 10 machines have been optimized using the Citrix Optimizer with the recommended template for Windows 10 2004. Please note, the template can be downloaded form the template marketplace in the Citrix Optimizer.
The following scenarios are defined for this research:
- Windows 10 1809, 17763.864, as the baseline;
- Windows 10 1903, 18362.476;
- Windows 10 1909, 18363.476;
- Windows 10 2004, 19041.207.
All tests are done using our standardized testing methodology, which is described here.
Expectations and results
When executing these kinds of researches there is always an expectation. Based upon previous Windows 10 researches it is expected that Windows 10 2004 will result in a slightly lower user capacity, caused by a higher resource utilization. This is because of continuously added features.
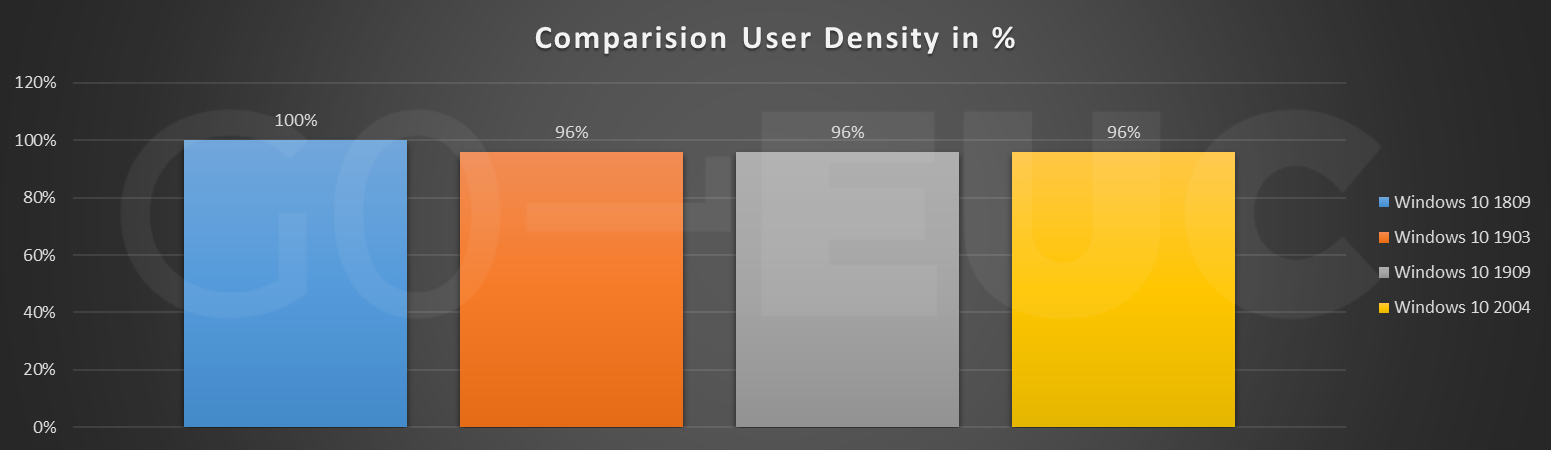
The user density is determined based on a CPU threshold. As the CPU threshold is reached, it is possible to calculate the active users on the system. This is not a recommend method as other factors can influence the user density of the environment. Based on previous researches it is known that the GO-EUC environment is limited by CPU, so therefore this method is used for now.
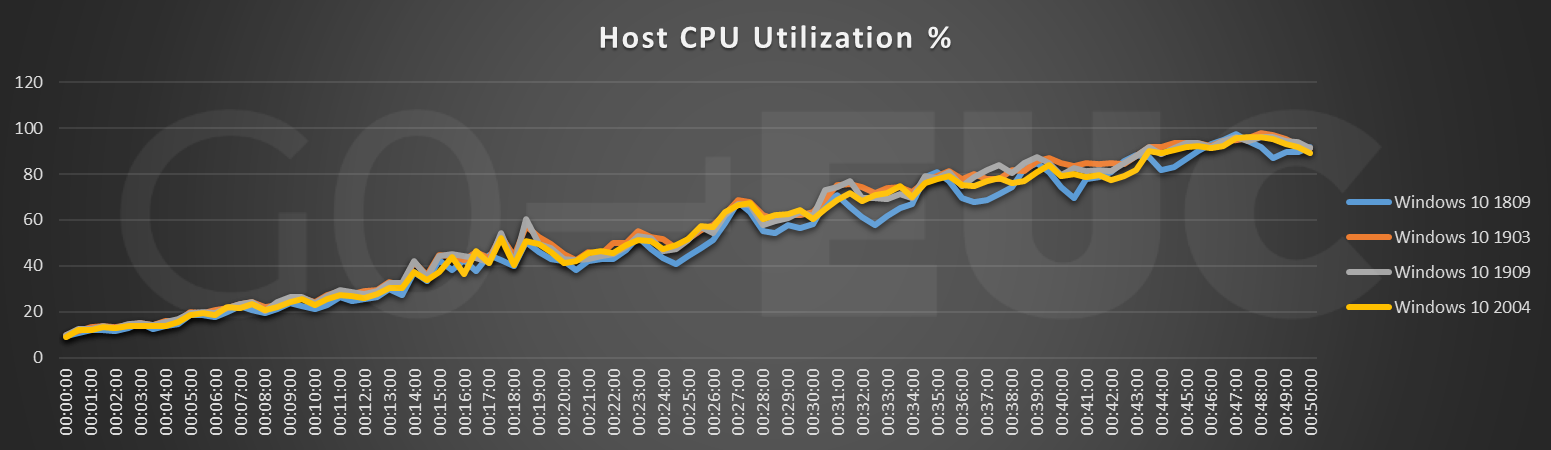
Higher is better
The pattern between the different Windows 10 versions is changing. Previous researches have shown a decrease in capacity, which is not confirmed in this research. If it comes to user density for Windows 10 2004, there is no difference between the two previous versions. Comparing with the baseline it is four percent. Take into account that build 1809 is two years old and, in that time, new CPUs have been released. CPUs which are more powerful and could easily handle the four percent impact.
Lower is better
Lower is better
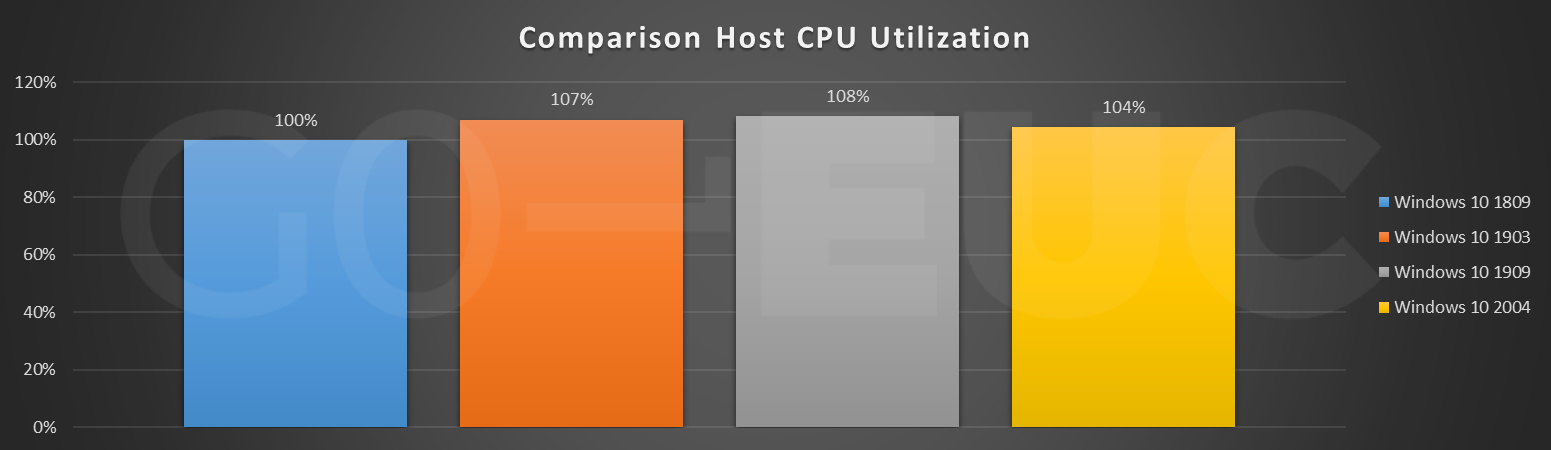
Concerning CPU Utilization Windows 10 2004 looks slightly more promising than the two previous builds, 1903 and 1909. Compared to Windows 10 build 1809, there is a small increase of four percent.
Lower is better
Lower is better
Lower is better
Lower is better
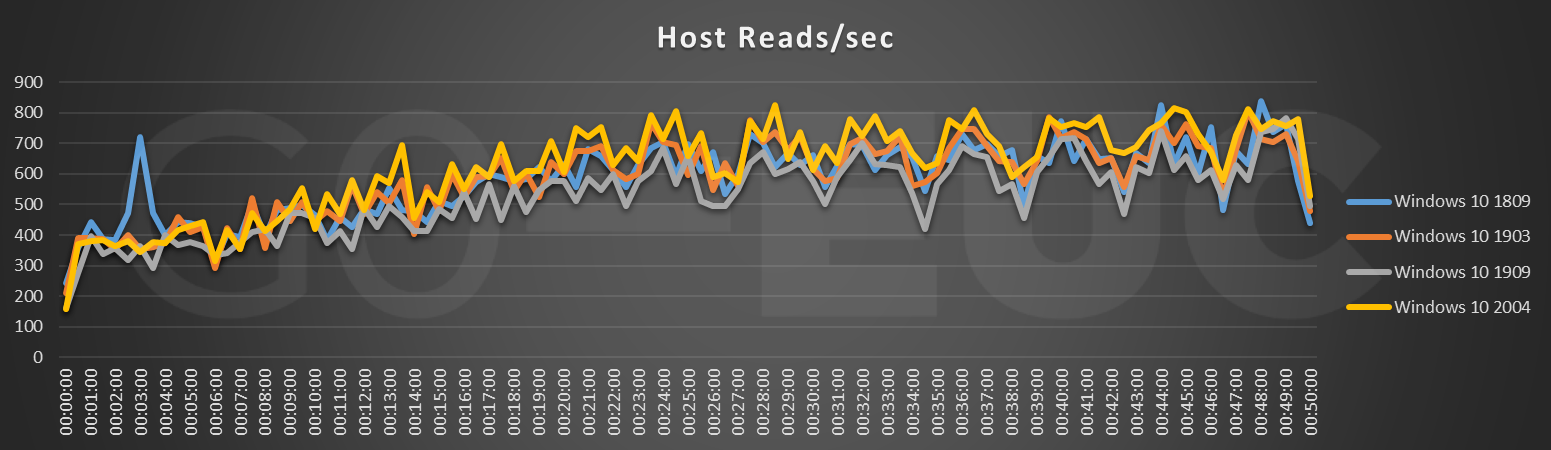
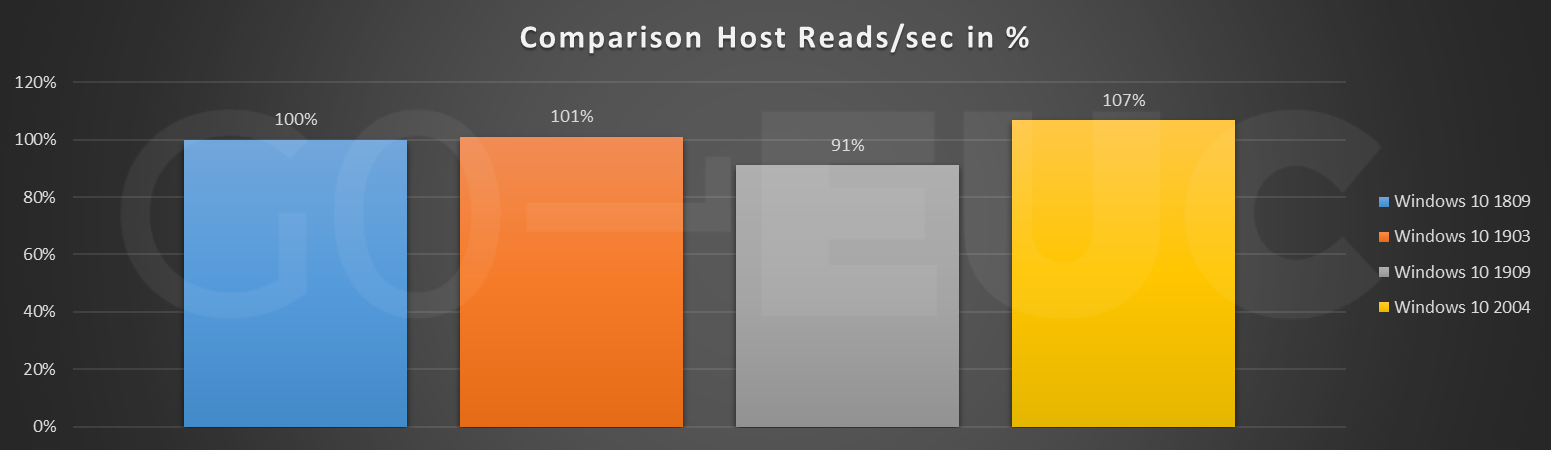
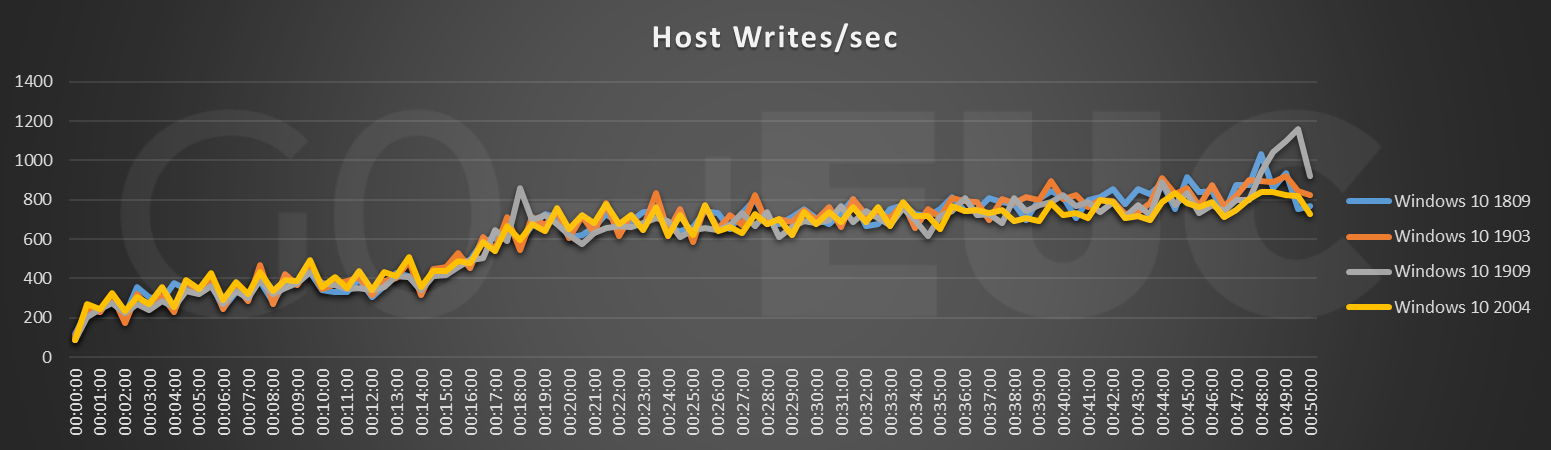
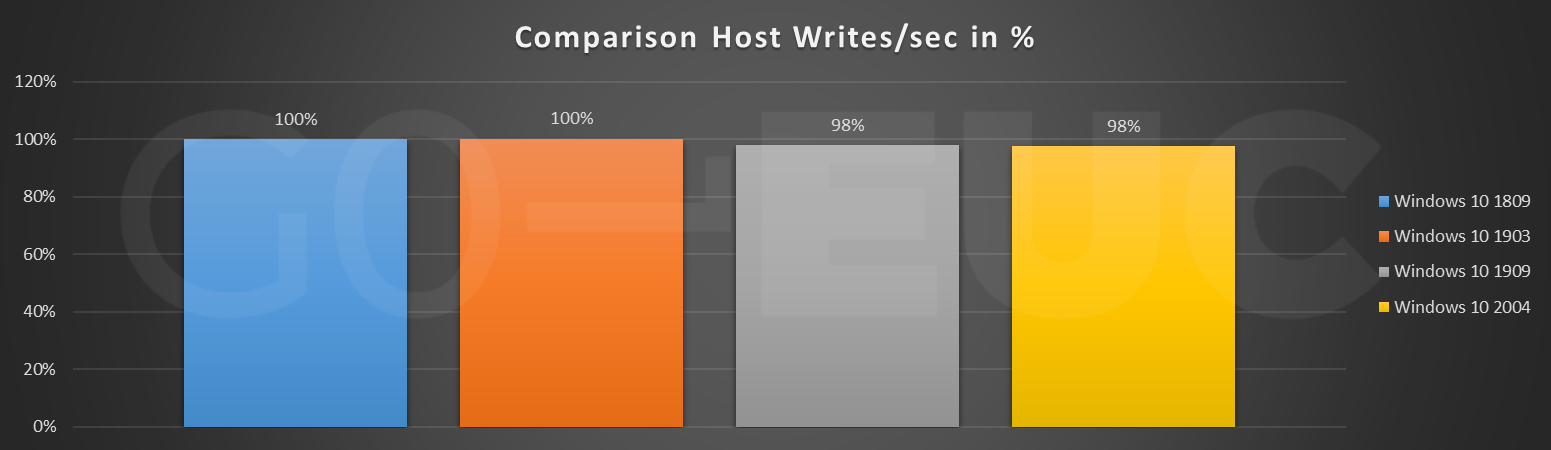
Looking at the Host Reads/sec line chart, the pattern is quite similar compared to Windows 10 1809. Nonetheless it can be seen that the Windows 10 2004 is overall slightly higher compared to previous builds. Even though this is higher, this would most likely not be noticeable as the increase is not significantly high. Also depending on which VDI solution is used (and even storage), reads are most of the time cached in some kind of way.
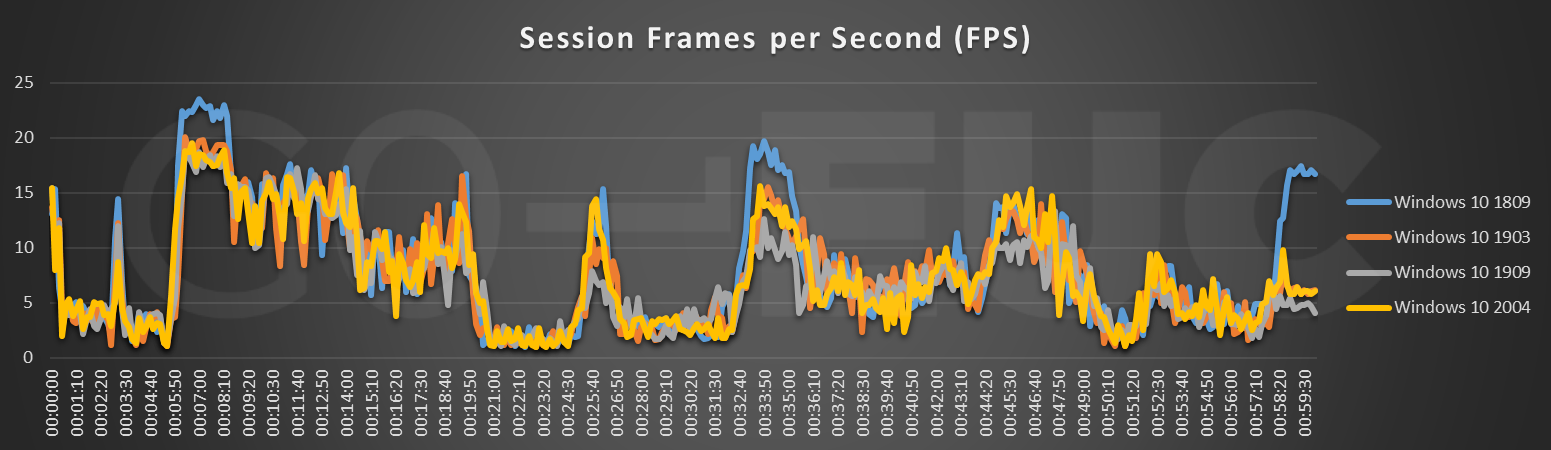
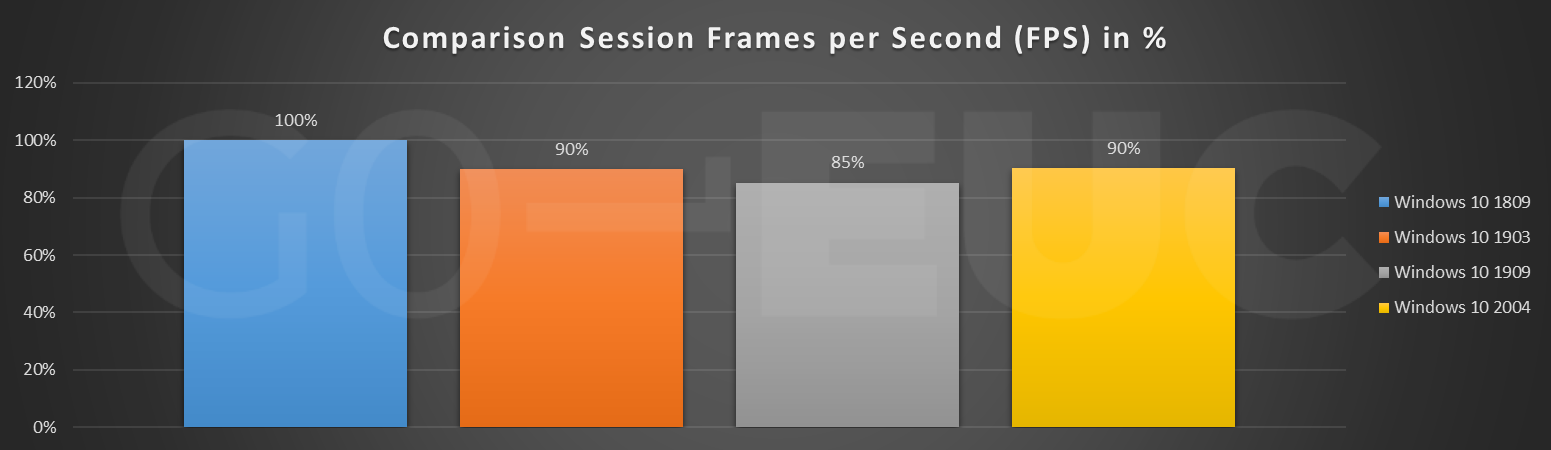
Session Frames per Second (FPS) is an indicator of the user experience. A previous conducted research has shown FPS is not the most reliable metric.
Higher is better or lower is better, does not apply. The FPS for video content will be different (higher) than when reading a Word document (lower). That is normal behavior. Nonetheless for heavy graphical workloads it could be noticeable. For normal VDI users, this decrease will not be noticeable. Please note, the spike at the end of the line chart heavily influences the average of the comparison.
Lower is better
Lower is better
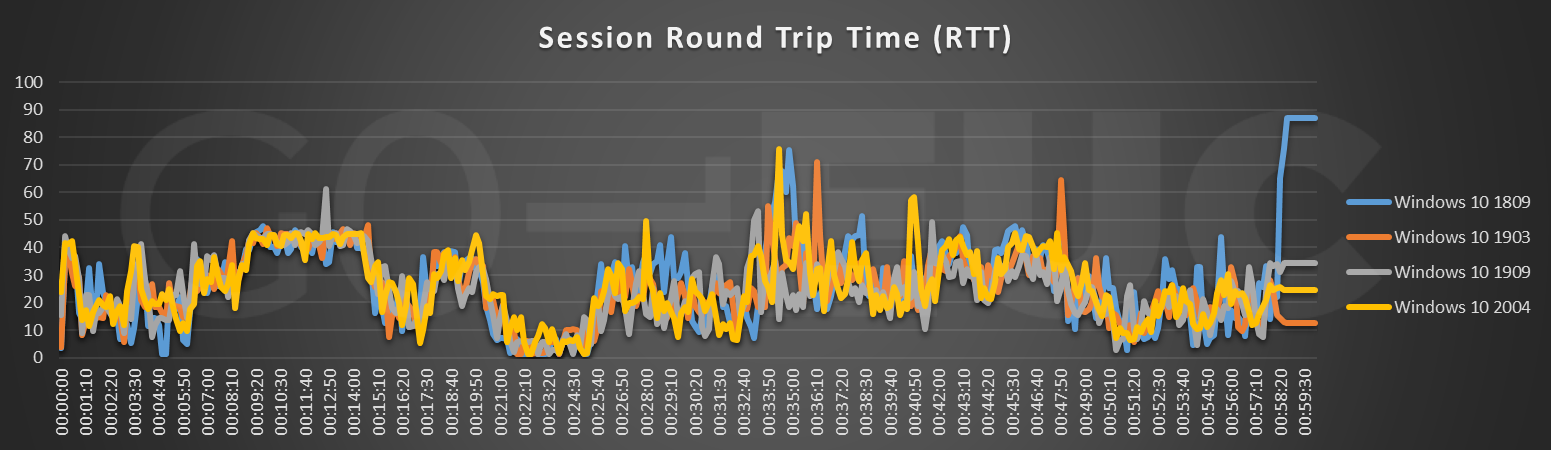
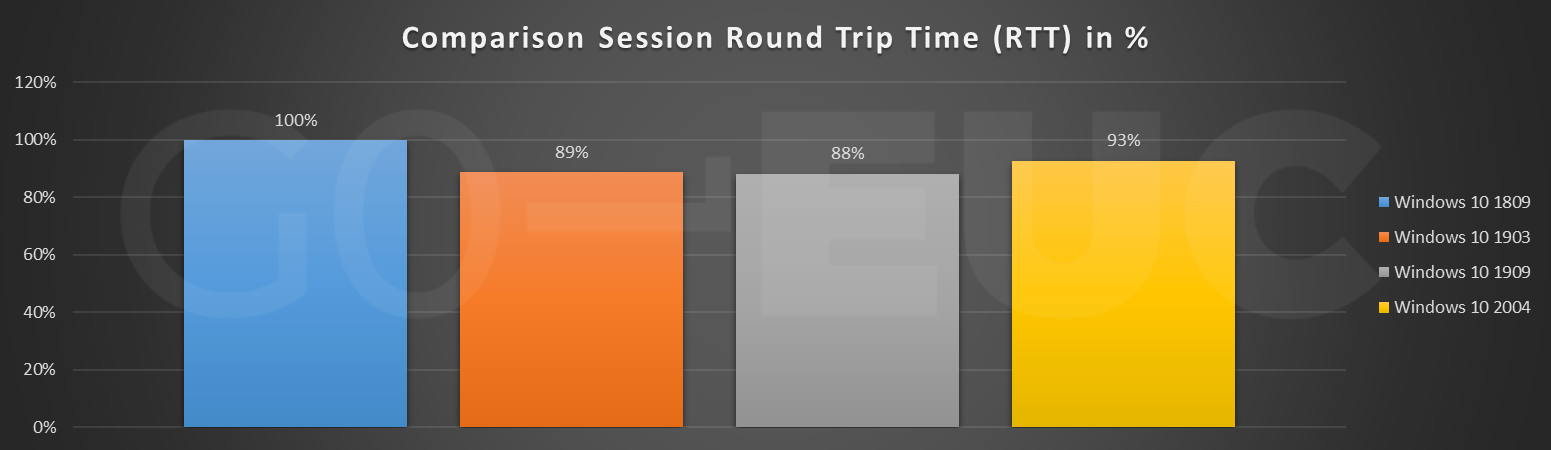
Round Trip Time (RTT) is the elapsed time from when the user hits a key until the response is displayed back at the endpoint. The user protocol is the ICA protocol. Looking at the line chart the behavior looks the same with each build. When the bar chart is taken into account, it is clearly seen that the RTT has decreased.
| Windows 10 version | Round Trip Time (RTT) value |
|---|---|
| Windows 10 1809 | 28 |
| Windows 10 1903 | 25 |
| Windows 10 1909 | 25 |
| Windows 10 2004 | 26 |
Looking at the raw data of Windows 10 1809 and Windows 10 2004 it’s a difference of 3 milliseconds. A difference that small in milliseconds is not noticeable to an end user in a VDI. Like the FPS chart, the spike at the end heavily influence the average of the comparison.
Lower is better
Lower is better
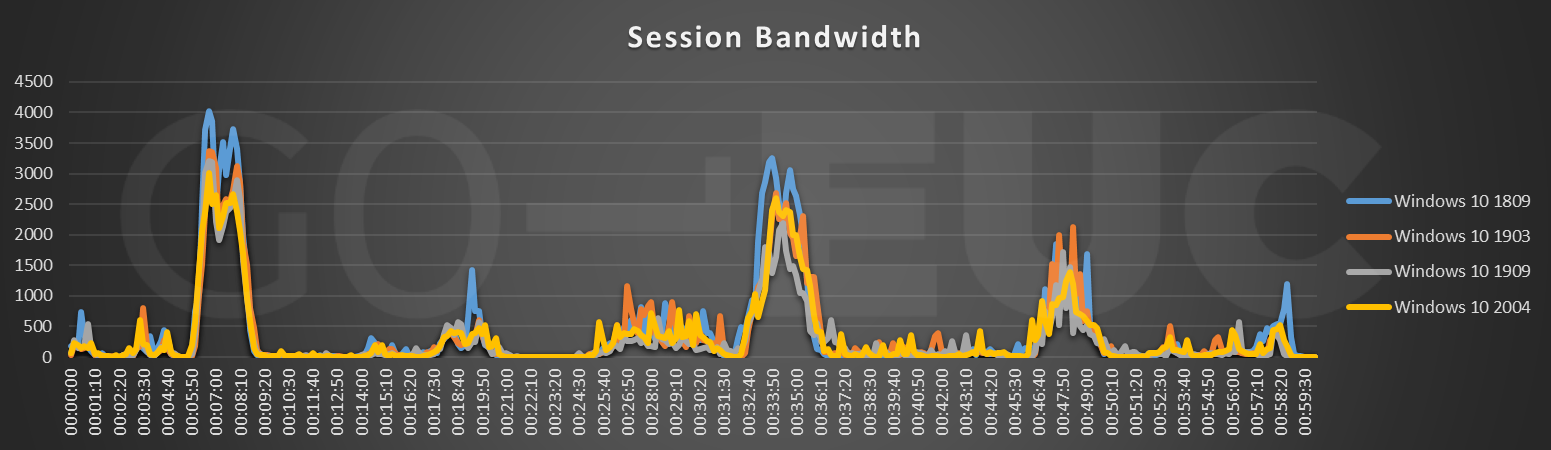
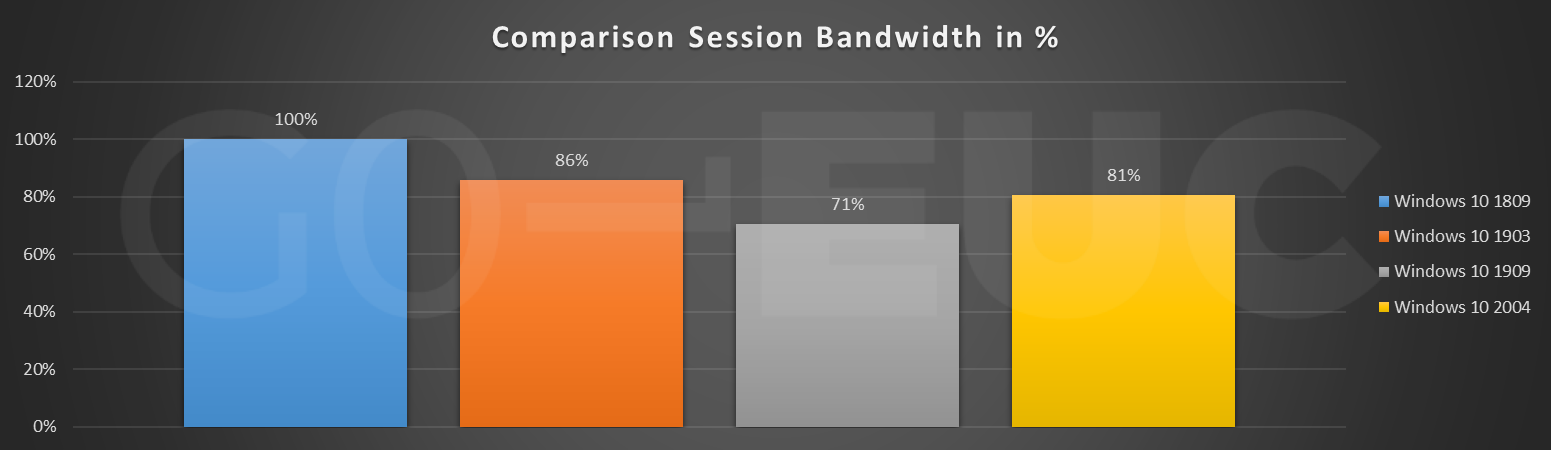
Windows 10 2004 is more efficient with bandwidth compared to Windows 10 1809 and less efficient compared to the Windows 10 1909. At this point it not clear what is causing the difference in the bandwidth, but could be related to theme of Windows 10. Think of the small optimization in the Windows start menu but also the change of background and the taskbar color.
Please note: the session bandwidth is the bandwidth consumed by the remoting protocol, which is in this case Citrix ICA.
Conclusion
As with each Windows 10 Edition new features and functionalities are introduced and (security) improvements are implemented to create a better and more stable Windows 10 edition. The GO-EUC platform has tested almost all Windows 10 builds. With all the conducted researches on Windows 10 it looks like the last three builds are similar when it comes to performance in general.
If the results are compared with each other, it looks like the performance does not have metrics that decreases or increases significantly. And when comparing to the baseline Windows 10 1809, there is a slightly negative impact. On the other hand, that build is almost two years old and as written previously in this research, hardware evolves too. Meaning CPUs are more powerful. Memory and caching techniques are optimized and developed as well.
What could be the case that the performance of the last three Windows 10 versions are quite stable and have a similar user density? In this recent blog, performance issues concerning slow boot times are elaborated for Windows 10 when installing a specific Windows Update. It could be possible that for Windows 10 one or more updates has been released which applies on at least the latest three versions, which results in stable performance. It would be interesting to conduct a research with vanilla Windows 10 version, meaning there are no updates installed.
To conclude Windows 10 2004 has no significant performance impact and is quite similar regarding the previous Windows 10 versions. Nonetheless upgrading within an organization has always an impact. For example for your applications. It is highly recommended to validate the performance of Windows 10 and have a strategy to update to a specific Windows 10 version. Bear in mind, that Windows 10 has a feature update twice a year and upgrading to each build will have a huge impact on your business and day-to-day administration.
Are you deploying each version of Windows 10 within your organization to keep up with latest features or are you deploying the fall editions for longer support?
Let us know in the comments below or share it on the Slack channel.
Photo by Meriç Dağlı on Unsplash